 |
| 1. ** How to search the site? ** |
| 2. ** I lost my dealer username / password? ** |
| 3. ** I want to be a Roline Dealer? ** |
| 4. ** Where is the nearest Roline Shop? ** |
| 5. Fibre Optic Cables? |
| 6. Roline UPS differences |
| 7. UTP, FTP, S/FTP cables - what's the difference? |
| 8. What is Gender Changer? |
| 9. What is KVM Extender? |
| 10. What is KVM Switch? |
| 11. What is Video Splitter? |
| 12. What means AWG? |
| 13. Which is the longest VGA cable? |
|
 |
 ** How to search the site? ** ** How to search the site? ** | top |
|
roline-bg.com has a product base containing more
than 1000 different articles and sometimes is difficult to find the product
you are looking for.
Here takes part our search engine. How
to use it...
|
 |
 ** I lost my dealer username / password? ** ** I lost my dealer username / password? ** | top |
|
Please call: +359 2 / 816-49-18 or mail to: v.vassilev@comelsoft.com
|
 |
 ** I want to be a Roline Dealer? ** ** I want to be a Roline Dealer? ** | top |
|
Please call our hotline number: 02 / 816-49-11 or mail your question to: info@comelsoft.com
|
 |
 ** Where is the nearest Roline Shop? ** ** Where is the nearest Roline Shop? ** | top |
|
Contact Roline dealer near you:
Bulgarian Roline Dealers
|
 |
 Fibre Optic Cables? Fibre Optic Cables? | top |
|
 Fiber
optic (or "optical fiber") refers to the medium and the
technology associated with the transmission of information as light impulses
along a glass or plastic wire or fiber. Fiber
optic (or "optical fiber") refers to the medium and the
technology associated with the transmission of information as light impulses
along a glass or plastic wire or fiber.
Fiber optic wire carries much more information than conventional copper
wire and is far less subject to electromagnetic interference. Most telephone
company long-distance lines are now fiber optic.
Transmission on fiber optic wire requires repeating at distance intervals.
The glass fiber requires more protection within an outer cable than copper.
For these reasons and because the installation of any new wiring is labor-intensive,
few communities yet have fiber optic wires or cables from the phone company's
branch office to local customers (known as local loop).
For additional information we suggest the following site:
Fiber Optic
Tutorial
Product Pages: Roline
Fiber-Optic Patch Cables
|
 |
 Roline UPS differences Roline UPS differences | top |
|
Roline UPS (Uninterruptable Power Supply) devices fall in three
main categories specified by its topology and the following 'voltage
phenomenoms' they protect against:
1. Outage-Blackouts; 2. Sags/brownouts; 3. Dynamic Overvoltage; 4. Undervoltage;
5. Overvoltage; 6. Lightning; 7. Transients (Surge); 8. Frequency Variations;
9. Voltage Distortion hf (Burst); 10. Voltage Harmonics
Category 3: Covers the devices from
the Personal Secure product line.
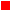
These UPSs are also known as Off-Line orVFD (Voltage & Frequency
Dependant). These are cost-effectrive solutions for SOHO users. Protect
agains situations 1 to 3 shown above.
Category 2: These are devices from
the Line Secure product line.
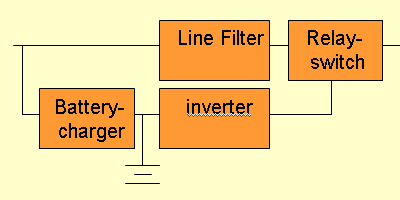
Also known as Line-Interactive or VI (Voltage Independant) these
devices are intended for these users who want more protection than Off-Line
devices can offer, but do not want to pay for the real double-conversion
UPS from Category 1. Line-Secure Series gives the user true Sine-Wave
output, Advanced Battery Management and reliable shutdown solution
Protects against situations 1 to 5.
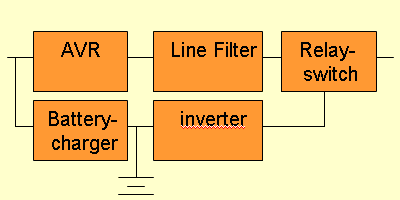
Категория 1: Devices in the Pro
Secure product line.
Also called On-Line, Real Double-Conversion, or VFI (Voltage
& Frequency Independant). This is the most reliable solutions
for projects from any scale, protecting your equipment agains any of the
above power-line disturbances.
Pro Secure means total independence and complete isolation between input
and output for voltage and frequency. This double conversion topology
is recognized as industry's most reliable topology available now.
Product pages: Roline
UPS Devices
Power Point Presentation
|
 |
 UTP, FTP, S/FTP cables - what's the difference? UTP, FTP, S/FTP cables - what's the difference? | top |
|
The network patch cables Category 5е (Cat. 5e) are used for structured
building cabling for applications strating from 100 to 250 MHz.
All three consist of 8 copper wires (AWG-24 for UTP and AWG-26 for FTP/S-FTP).
What is the difference:
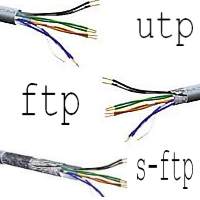 UTP
(Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables are unshielded, less-expensive cables.
They are more pliable to electromagnetic interferences and typically are
used in SOHO environments. UTP
(Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables are unshielded, less-expensive cables.
They are more pliable to electromagnetic interferences and typically are
used in SOHO environments.
FTP (Foil-screened Twisted Pair) cable is a cable containing multiple
pairs of copper wire enclosed in a sheath of aluminum foil. It's used
in wiring systems in buildings or other environments where heavy noise
adjacent to the wire might cause interference. The foil provides insulation
not afforded by UTP (unshielded twisted pair), the most common kind of
structural wiring. The disadvantage of FTP is that it requires somewhat
more care in "earthing" (grounding) than UTP and electrical
impedances must be matched when connecting to UTP.
S/FTP are the same as FTP but they have a copper braid in addition
to the aluminum laminated foil.
Product pages: Network
Patch Cables
|
 |
 What is Gender Changer? What is Gender Changer? | top |
|
 The
Gender Changer is a simple adapter which allows a cable and port
with same interface to be connected together. The
Gender Changer is a simple adapter which allows a cable and port
with same interface to be connected together.
For example - if you have a video cable with two 15-pin male connectors
and KVM switch with the same male connector, you will be unable to link
them. Here takes place our Gender Changer with two 15-pin female connectors.
Gender Changers are of various types - 9, 15, 25-pole, Centronics, USB...
Product Pages: Roline
Gender Changers
|
 |
 What is KVM Extender? What is KVM Extender? | top |
|
The KVM Extender system consist of two devices - transmitter and
receiver allowing for operating a single computer system remotely - trough
the existing networking cable. The maximum operating distance may vary
depending on the cable type - it is approx. 110 meters with standard Cat.
5 cables.
The Receiver unit is connected to the computer with cables for video,
keyboard and mouse and to the receiver unit trough the network cable.
The receiver on other hand, has connectors for the Monitor, Keyboard and
Mouse which control the remote computer.

Product Pages:
Roline KVM Extenders
|
 |
 What is KVM Switch? What is KVM Switch? | top |
|
KVM switch is short for keyboard, video, mouse switch,
a hardware device that enables a single keyboard, video monitor and mouse
to control more than one computer one at a time.
KVM switches are popular among users who have upgraded their home PC systems
and want to still use their old computers but do not want to invest in
a second keyboard, monitor and mouse. KVM switches are also used by business
to save money when one person uses more than one computer and in server
farms where it is only necessary to periodically access each separate
server in the farm one at a time.
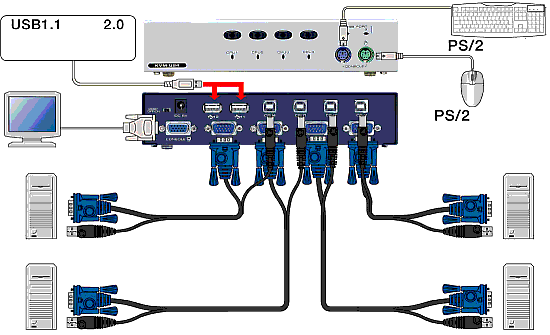
A typical KVM Switch has appropriate number of KVM inputs (2, 4, 8, 12,
16) for connecting the mice, keyboards and videocards of the machines,
and single input for the keyboard, mouse and monitor used as a console.
KVM devices are highly varied - some offer keyboard and mouse emulation,
which means that all the connected computers can be booted simultaneously
(in case of power failure for example).
The switching takes place manually (with keys on the switch) or
automatically (with keyboard shortcuts or on time intervals - which
is extremely useful with security systems consisting of multiple computers)
Some KVM Switches has OSD menus for control and status and RackMount
casings.
Other support daisy chaining which means that many switches can
be connected one after another thus increasing the number of computers
which can be managed from a single console.
Product Pages: Roline KVM Switches
manual / automatic
Product Pages: Roline
KVM cables
|
 |
 What is Video Splitter? What is Video Splitter? | top |
|
| The Video Splitter (also called Video Distributor) is a device that allows the video output from one computer to be displayed simultaneously on
multiple VGA monitors - 2, 4, 8, 16... It is a useful solution for presentations and surveillance applications.
Product Pages: Roline Video Distributors
|
 |
 What means AWG? What means AWG? | top |
|
American Wire Gauge (AWG) is a U.S. standard set of non-ferrous
wire conductor sizes. The "gauge" means the diameter. Non-ferrous
includes copper and also aluminum and other materials, but is most frequently
applied to copper household electrical wiring and telephone wiring. Typical
household wiring is AWG number 12 or 14. Telephone wire is usually 22,
24, or 26. The higher the gauge number, the smaller the diameter and the
thinner the wire. Since thicker wire carries more current because it has
less electrical resistance over a given length, thicker wire is better
for longer distances. For this reason, where extended distance is critical,
a company installing a network might prefer telephone wire with the lower-gauge,
thicker wire of AWG 24 to AWG 26.
AWG is sometimes known as Brown and Sharpe (B&S) Wire Gauge
Product pages: Network
Patch Cables
|
 |
 Which is the longest VGA cable? Which is the longest VGA cable? | top |
|
The longest available VGA cables are 50 meters long:
11.04.5250-2,
11.04.5299-2,
11.04.5350-2,
11.04.5399-2
|
 |